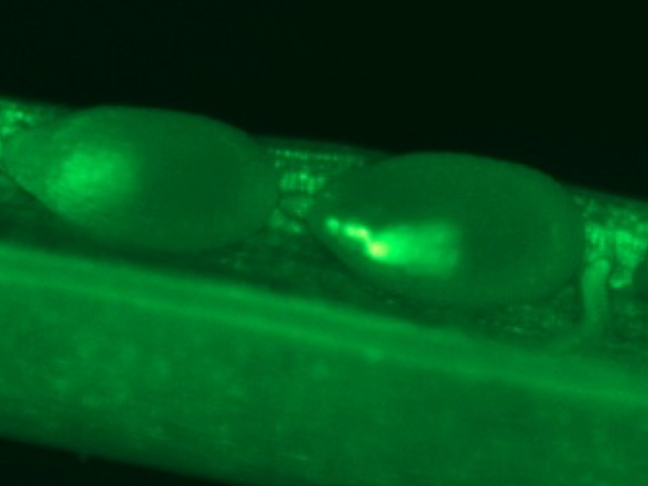
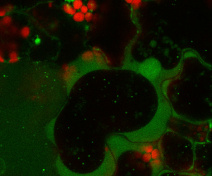
The SATURNE team brings together experts in molecular physiology who are interested in the molecular processes of nutritional recycling and the allocation of nitrogen resources in the plant organs.
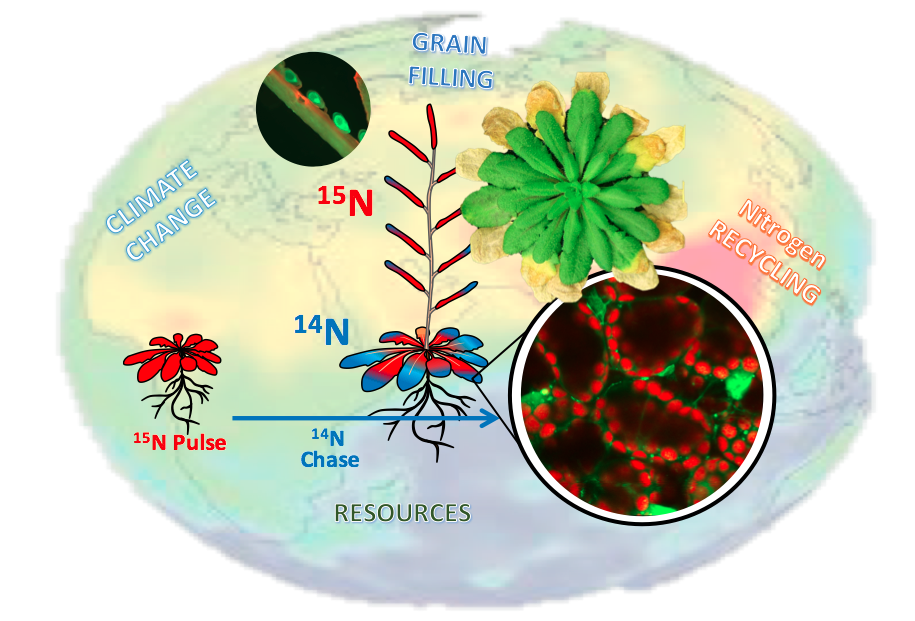
The team's goal is to explain how plants recycle their nutrients, and how this metabolism contributes to productivity and seed quality by improving nitrogen use efficiency. The study of the fundamental molecular mechanisms of autophagy and proteolysis during the aging of plant organs is at the center of this research. The dissection of the genetic bases regulating the remobilization of nutrients for grain filling completes the mechanistic study by providing an approach without a priori at the whole plant level.
Biological Questions
The major research questions of the SATURNE team are:
- How do the senescence autophagy and proteolysis mechanisms control the allocation of resources within the plant?
- What is the nature of autophagy protein substrates for recycling?
- Characterization of the specific autophagy actors involved in the response of plants to their environment.
- Contribution of nitrogen remobilization to the nutritional quality of grain.
- Contribution of nitrogen remobilization to plant adaptation to climate change.
- How to manipulate the recycling mechanisms in plants of agronomic interest with a view to more environmentally friendly crops?
Models, tools and methods
The team studies the metabolism and physiological mechanisms of nitrogen remobilization at the scale of the whole plant (nitrogen flux), the organ (enzymology, metabolome, proteome) and the cell (genes, traffic vesicular, autophagic activity).
The work is carried out on different genotypes of Arabidopsis (mutants and natural accessions) and cultivated plants (barley and wheat).
The methodological approaches used are:
Functional analysis of the actors involved in autophagy and nutritional recycling
Measurement of autophagic activity
Measurement of nitrogen fluxes at the whole plant level by 15N isotopic tracing
Leaf senescence phenotyping
Analysis of primary metabolism in multiomics
Interactions genotype-environment and natural variability
Societal and economical impacts
The work of the SATURNE team responds to the following societal and economic questions:
Nitrogen use efficiency and fertilizer reduction in agriculture.
Seed quality and protein content.
Nutritional adaptation of plants to the vagaries of climate change.
Nitrogen use efficiency and fertilizer reduction in agriculture.
Seed quality and protein content.
Nutritional adaptation of plants to the vagaries of climate change.

Leaders:
Céline Masclaux-Daubresse
Fabien Chardon