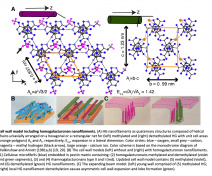
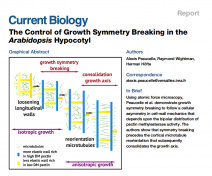
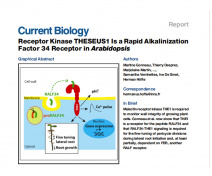
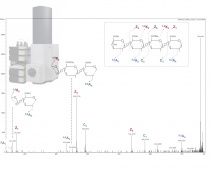
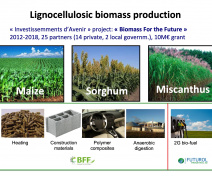
The team is studying the architecture and metabolism of cell walls in relation to cell expansion, immunity and as a source of natural defense stimulators in plants. It also contributes to the improvement of lignocellulosic biomass crops such as miscanthus.
Biological Questions
1. How do plant cells grow in terms of cell wall architecture and metabolism ?
2. How does the cell wall metabolism contribute to plant immunity ?
3. How to improve the industrial quality of lignocellulosic biomass feedstocks, in particular that of the perennial grass miscanthus ?
Models, tools and methods
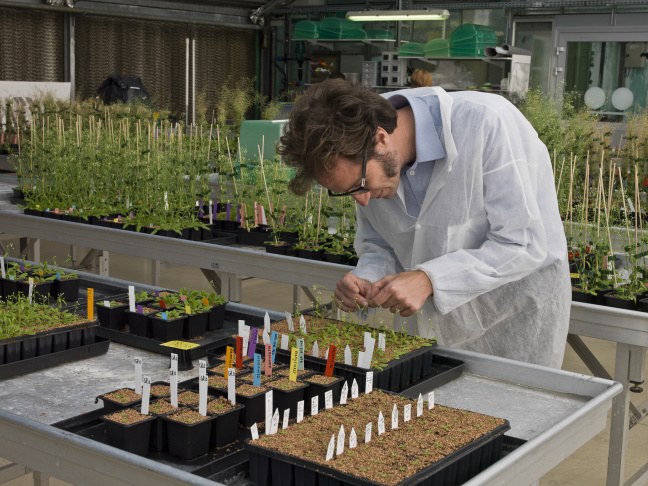
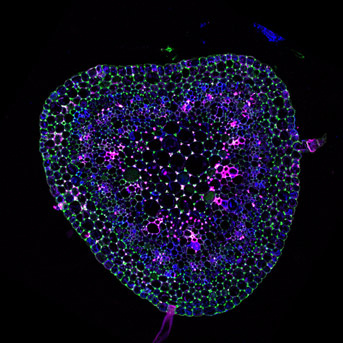
Models : we use Arabidopsis thaliana (Fig. 1) and Physcomitrium patens as model plants and Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum higginsianum as necrotrophic and hemibiotrophic fungal pathogens respectively. We also study the perennial energy grass miscanthus
Tools : Molecular genetics, protein biochemistry, carbohydrate chemistry and oligosaccharide profiling, live cell imaging using genetically encoded sensors and root microfluidics, super resolution microscopy on immuno-labeled cell wall components, atomic force microscopy to study cell wall mechanics in vivo, FTIR imaging, kinematic growth analysis, finite element modeling
Societal and economical impacts We believe that the study of the plant cell wall is interesting because the assembly and remodelling of this complex polymer network are key processes governing plant growth and morphogenesis. In addition, cell walls contribute to signaling in response to changes in the abiotic and biotic environment. Plant cell walls are also critical components of food and feed and a sustainable source of materials, chemicals and energy. Finally, plant cell walls provide a source of inspiration for the conception of new nanomaterials.
1. How do plant cells grow in terms of cell wall architecture and metabolism ?
2. How does the cell wall metabolism contribute to plant immunity ?
3. How to improve the industrial quality of lignocellulosic biomass feedstocks, in particular that of the perennial grass miscanthus ?
Models, tools and methods
Models : we use Arabidopsis thaliana (Fig. 1) and Physcomitrium patens as model plants and Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum higginsianum as necrotrophic and hemibiotrophic fungal pathogens respectively. We also study the perennial energy grass miscanthus
Tools : Molecular genetics, protein biochemistry, carbohydrate chemistry and oligosaccharide profiling, live cell imaging using genetically encoded sensors and root microfluidics, super resolution microscopy on immuno-labeled cell wall components, atomic force microscopy to study cell wall mechanics in vivo, FTIR imaging, kinematic growth analysis, finite element modeling
Societal and economical impacts We believe that the study of the plant cell wall is interesting because the assembly and remodelling of this complex polymer network are key processes governing plant growth and morphogenesis. In addition, cell walls contribute to signaling in response to changes in the abiotic and biotic environment. Plant cell walls are also critical components of food and feed and a sustainable source of materials, chemicals and energy. Finally, plant cell walls provide a source of inspiration for the conception of new nanomaterials.
Leader:
Kalina T Haas