IJPB Highlights from Life Sciences at Paris-Saclay University
IJPB Plant Platforms Focus at the Plant Observatory: 6 Platforms Serving Plants and More!, 9/24/23
The Plant Observatory (OV) is a unique collection of resources dedicated to phenotyping plants at multi-levels. The goal of the OV is to establish an integrated, high-throughput analysis of plants that combines macroscopic, biochemical, cytological, chemical, and metabolic phenotyping. It relies on 6 components: Biochemistry (led by Hakim Mireau), Chemistry/Metabolism (led by Grégory Mouille), Plant Cultivation (led by Hervé Vaucheret), Cytology/Imaging (led by Bertrand Dubreucq & Samantha Vernhettes), Phenoscope (led by Olivier Loudet), and the Versailles Arabidopsis Stock Center (led by Christine Camilleri).
> More
Jean-Christophe Palauqui is the new head of the OV as of October 1, 2023.
Plant Mitochondrial Translation Initiated by Protein-RNA Interaction, 9/8/23
Although all mitochondria share a common ancestor, the protein complexes essential for their function have diverged significantly among eukaryote croups. In a study published in the journal Science, a consortium of researchers including the "Organelle and Reproduction" team, OrgaRepro,of Hakim Mireau, highlighted the crucial role of mTRAN proteins in initiating translation in plant mitochondria of Arabidopsis thaliana. They may facilitate translation initiation by directing ribosomes.
> More
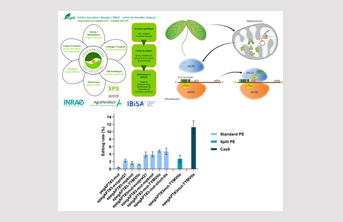
Improvement of Prime Editing, the Ultimate Genome Editing Tool, in the Moss Model Physcomitrium patens, 7/5/23
Prime Editing, a tool based on the CRISPR-Cas9 approach, achieves unprecedented accuracy among genome editing tools available today, but its efficiency can still be improved. Researchers from the "DNA Repair and Genome Engineering" DRAGON team have developed a method to improve Prime Editing in the model plant Physcomitrium patens. They evaluated the use of a plant-derived reverse transcriptase. For the first time, Prime Editing is functional in plants by expressing the two subunits of the prime editor, nCas9 and reverse transcriptase, as two independent peptides. This split Prime Editing will facilitate testing of new domains in plants.
> More
Back